Every year millions of Americans suffer from Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a long term lung disease that causes breathing problems. COPD is preventable, and early detection helps in treatment. Read on to understand all about the symptoms and treatments available for COPD.
What is COPD
COPD is an obstructive pulmonary disease that gets worse over time. This disease includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, with both conditions occurring together and varying in severity. In patients with COPD, inflammation of the airways, and damage to lung tissue causes difficulties in breathing.
Causes of COPD
Long term exposure to airborne irritants generally causes COPD. Sustained exposure to fumes from burning fuels and cigarette smoke is the highest contributing factor to COPD. Other risk factors could include:
– Genetics
– Occupational exposure to chemicals and dust
– Pre-existing diseases such as asthma
Symptoms and Signs of COPD
In the early stages, COPD does not show significant signs. As the disease progresses, symptoms you may notice are:
– Wheezing
– Shortness of breath
– Tightness in the chest
– Persistent cough
– Lethargy
– Swelling in lower extremities
– Unintended weight loss
– Frequent lung infections
Diagnosis of COPD
After reviewing your symptoms and medical history, your doctor may advise several tests to reach a conclusive diagnosis. Some of these might be a:
– Chest X-ray
– Lung Function test
– Arterial blood gas analysis
– CT scan
Treatment
As cigarette smoke is the leading cause of this disease, the primary form of treatment centers around quitting all types of smoking.
Doctors may prescribe a course of medications in the form of inhalers to help ease the symptoms and help you breathe easier.
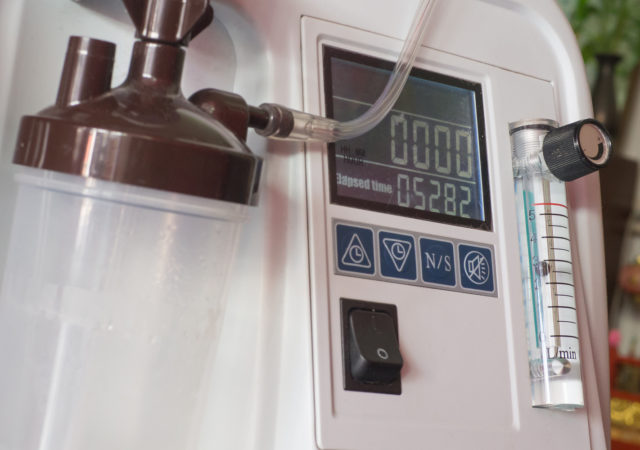
Lung therapies such as oxygen therapies and intensive lung rehabilitation programs could benefit people with moderate or severe COPD.
Home use of noninvasive ventilation devices with masks has also shown to help provide relief.
For severe cases often, surgery is the best treatment option. Some of the surgical options involve:
– Lung transplant- Complete replacement of lungs.
– Bullectomy – Removal of large air spaces in the lungs.
– Lung volume reduction – Surgical removal of damaged tissues from the upper lung.
Through early detection and effective treatment, people with COPD can attain success at reducing symptoms. While COPD is not curable, with efficient management, most people can achieve a better quality of life.